- HOME
- Story of the Cover
Story of the Cover
Polymerization and stability of actin conjugated with polyethylene glycol
(Masaya Sagara, Kuniyuki Hatori, Biophysics and Physicobiology 22, e220017 (2025), DOI: 10.2142/biophysico.bppb-v22.0017)
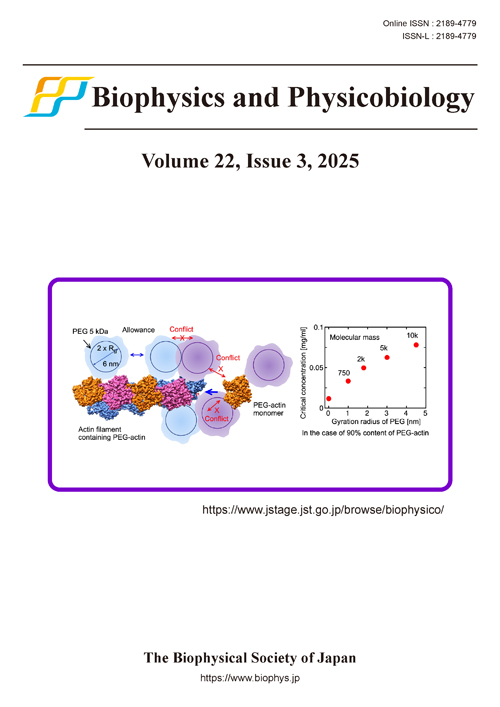
PEGylation, the conjugation of PEG (polyethylene glycol) to therapeutic agents such as proteins, has been exploited in the pharmaceutical field due to its ability to improve pharmacokinetics in vivo. To ascertain the impact of PEGylation on protein-protein interactions, we investigated the polymerization of PEG-conjugated actin using fluorescence spectroscopy in vitro. A high concentration of PEG-conjugated actin considerably suppressed its association due to PEG hinderance of C-terminus of actin and interferences between the PEGs on actin filaments (left panel). The critical concentration corresponding to the dissociation constant increased with increasing PEG size, providing insight into the repulsive energy of PEG conjugation against actin polymerization (right panel).
 Biophysics and Physicobiology
Biophysics and Physicobiology